- Submissions

Full Text
Gastroenterology Medicine & Research
Colonic Fistula Secondary to Acute Pancreatitis: A Case Report
Qiaodong Xu, Songgang Gu, Jiahong Liang, Shaodong Zheng, Zhihua Lin Peidong Zhang and Jiang Yan*
Department of Biliary-Pancreatic minimally invasive Surgery, China
*Corresponding author: Jiang Yan, Department of Biliary-Pancreatic minimally invasive Surgery, China
Submission: December 18, 2018Published: January 22, 2019

ISSN 2637-7632Volume2 Issue4
Abstract
Colonic fistula is rare after acute pancreatitis but is associated with a high mortality. In the current study, we describe a case of colonic fistula in a 39-year-old woman secondary to severe acute pancreatitis. Abdominal CT showed the presence of pancreatic pseudocysts. After percutaneous drainage was performance, yellow feculent liquid fluided from the drainage tubes. Subsequently, fistulography via drainage tube showed the presence of a colonic fistula into the descending colon. She was successfully treated by a colectomy for colonic fistula and drainage of the pancreatic pseudocysts. Although Colonic fistula is an infrequent complication of pancreatitis, clinicians should be aware of it because of its high mortality.
Keywords:Acute pancreatitis, Colonic fistula, Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Abbreviations:AP: Acute Pancreatitis; CT: Computed Tomography; ERCP: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio Pancreatography; EST: Endoscopic Sphincterotomy; SAP: Severe Acute Pancreatitis
Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is one of the most common surgical acute abdomens. Most patients develop edematous pancreatitis, which can be cured under conservative treatment and without serious complications [1]. However, 10% to 20% of AP patients develop necrotizing pancreatitis with serious complications including gastrointestinal fistula, abdominal bleeding, pancreatic pseudocyst and so on [2]. Among these complications, digestive tract fistula is an important factor leading to death of patients. Colonic fistula is rarely observed during the clinical course of acute pancreatitis, but potentially fatal in some cases [3]. In this study, a case of colonic fistula result from severe acute pancreatitis was reported.
Case Report
In February 2017, a 39-year-old woman was admitted to the department of hepatobiliary surgery of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Medical College of Shantou University (Shantou, China) due to intermittent upper abdominal pain after eating greasy food. According to result of the abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan there, she was diagnosed to have severe acute pancreatitis. Percutaneous drainage was performance under the orientation of b-ultrasonography then peripancreatic and retroperitoneal drainage tubes were put. In March, the patient transferred to Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University (Guangzhou, China). After the treatment of Endoscopic retrograde cholangio panecreatography (ERCP) and endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST), her condition improved and discharged.
Figure 1:CT scan showing expansile pancreatic pseudocysts.
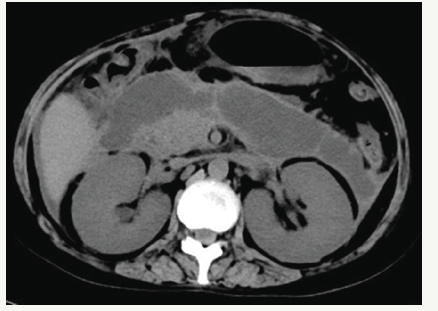
In June, she was admitted to our hospital because of persistent pyrexia. The laboratory data on admission showed that: white blood cell count (WBC) 16.11×10^9/L, C-reactive protein 67mg/L, which indicated the inflammatory reaction. Abdominal CT showed the presence of pancreatic pseudocysts and gall-bladder wall thickening (Figures 1 & 2), so percutaneous drainage was performanced. Yellow feculent liquid fluided from the drainage tubes. Thereby the bacterial, fungal culture and drug sensitivity experiments of the drainage were performanced. The result showed the presence of Enterococcus faecium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloacae. Subsequently, fistulography via drainage tube showed the presence of a colonic fistula into the descending colon (Figure 3). Due to the unsatisfactory effect of conservative treatment, surgery was scheduled. The patient subsequently underwent transverse colostomy in August.
Figure 2:CT scan showing gall-bladder wall thickening.
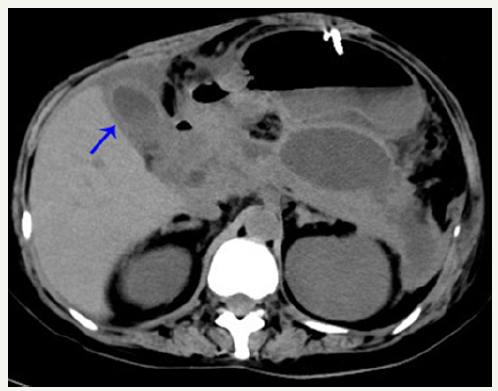
Figure 3:Fistulography via drainage tube showing the presence of a colonic fistula into the descending colon.
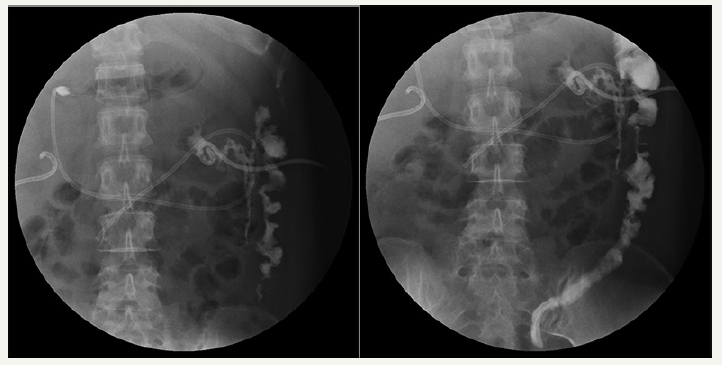
Figure 4:CT scan showing the disappeared pancreatic pseudocysts.
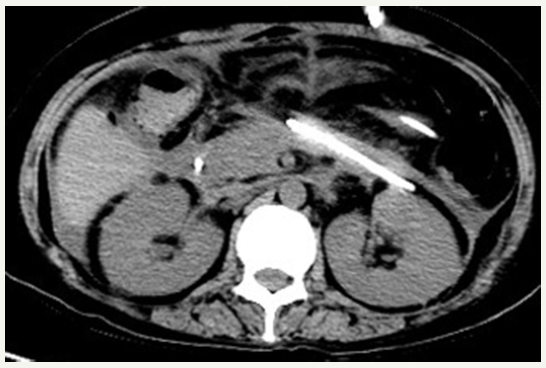
She recovered well after operation. The pancreatic pseudocysts gradually reduced (Figure 4). The symptom of pyrexia disappeared by repeat lavage through the drainage tube and the use of antibiotics. Her general condition improved and left our hospital on August 20.
Discussion
From an anatomical perspective, as the stomach, duodenum, jejunum and colon adjacent to the pancreas, peritoneal and retroperitoneal abscess will corrode adjacent intestinal wall firstly. Secondly, the fluid or abscess in abdominal cavity can oppress mesenteric blood vessels, leading to intestinal microcirculation disorders, resulting in ischemia and necrosis of intestinal wall [4]. Thirdly, debridement and other surgical procedures may cause mechanical damage to the intestine and increase the risk of intestinal fistula occurred [5]. Furthermore, the improper placement of drainage tube and long-term catheter drainage will oppress the intestinal tract and cause intestinal damage [6]. These are the main risk factors of the formation of intestinal fistula in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) patients.
SAP with intestinal fistula can be characterized by the stomach, duodenum, small intestine and colon fistula of single or multiple parts. Among them colonic fistula is most common, duodenal fistula, small intestine fistula, biliary fistula and gastric fistula are rare. Splenic flexure of colon fistula is the most common in colonic fistula. The reasons may be related to the weak blood supply of splenic flexure of colon, peripancreatic inflammatory violation and the destruction of the intestinal wall in the process of separating splenocolic ligament in debridement of the anterior approach [7]. The predilection site of duodenal fistula locate in pars horizontalis and descending part of duodenum, mainly because of pancreatic inflammation, intraoperative debridement operation, drainage tube compression and vacuum aspiration [8]. Small intestine fistula includes jejunum and ileal fistula, the reasons may be associated with intestinal abscess corrosion, a wide range of peritoneal abscess invasion and microcirculatory disturbance of mesenteric blood vessels caused by inflammation or abscess compression [9].
When purulent mucous liquid or yellow-green liquid or bilelike liquid fluids from the postoperative peritoneal drainage tubes in SAP patients and daily drainage liquid increases, or the nutrient solution dripping through nasogastric feeding tube are found in the drainage fluid, the possibility of intestinal fistula is need to be considered. After appropriate high-dose antibiotic treatment, unexplained repeated high fever and systemic symptoms of Gramnegative bacilli infection still happen, then intestinal fistula should be suspected as well [10]. Intake of methylene blue orally or by the nasogastric feeding tube and observation of methylene blue in the abdominal drainage tube will help to diagnose intestinal fistula. Gastrointestinal barium radiography or fistulography via abdominal drainage tube not only can make diagnose of intestinal fistula, but also help to make a general judgment on the site of intestinal fistula [11].
Patients with poor drainage after intestinal fistula are more likely to be complicated by severe infection. It is necessary to replace drainage tube as soon as possible. Only the fluent drainage will prevent abdominal infection and promote the fistula healing as soon as possible. In situation of high intestinal fistula with poor drainage, we can reposition drainage tubes by puncture or surgery, and place enterostomy tube in the distal end of the intestinal fistula. In situation of low intestinal fistula with poor drainage, reoperation may choose to operate enterostomy in the proximal end of the intestinal fistula and close the distal end of the intestinal fistula to transfer intestinal fluid out of the abdominal cavity, thereby reducing abdominal cavity inflammation. When the nutritional status of patients improves, and abdominal inflammation subsided, enterostomy closure can be operated. For patients with prolonged unhealed intestinal fistula, bowel resection of the fistula segment and intestinal anastomosis can be operated [12].
References
- Forsmark CE, Vege SS and Wilcox CM (2016) Acute pancreatitis. The New England Journal of Medicine 375: 1972-1981.
- Boumitri C, Brown E and Kahaleh M (2017) Necrotizing pancreatitis: Current management and therapies. Clin Endosc 50(4): 357-365.
- Merino Rodriguez E, Borobia Sanchez R, Ramia Angel JM, Rebolledo Olmedo S, de la Plaza Llamas R (2016) Spontaneous pancreatic-colonic fistula in a patient with severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol 39(3): 221-223.
- Belokonev VI, Katasonov MV, Kachanov VA, Katasonov VM, Iudin AE (2009) Gastrointestinal fistulaes in patients with pancreanecrosis. Khirurgiia (Mosk) (3): 61-64.
- Koutroumpakis E, Slivka A, Furlan A, Dasyam AK, Dudekula A, et al. (2017) Management and outcomes of acute pancreatitis patients over the last decade: A US tertiary-center experience. Pancreatology 17(1): 32-40.
- Topuzov EE, Balashov VK, Tsatinyan BG, Arshba EA, Petryashsmall AV, et al. (2017) Surgical treatment of acute pancreatitis: possibilities of percutaneous therapy. Khirurgiia (Mosk) (8): 91-94.
- Mohamed SR, Siriwardena AK (2008) Understanding the colonic complications of pancreatitis. Pancreatology 8(2): 153-158.
- Doi T, Wakabayashi N, Iwai N, Morita Y, Ogiso K, et al. (2013) Pancreatic pseudocyst with fistula to the common bile duct and the duodenum. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 110(7): 1288-1295.
- Jiang W, Tong Z, Yang D, Ke L, Shen X, et al. (2016) Gastrointestinal fistulas in acute pancreatitis with infected pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis: A 4-year single-center experience. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(14): e3318.
- Hwang SO, Lee TH, Park JW, Park SH and Kim SJ (2010) Endoscopic management of multiple colonic fistulae secondary to acute pancreatitis (with video). Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 71(2): 395-397.
- Tsou YK, Chu YY, Lin CH (2010) Education and imaging. Gastrointestinal: Spontaneous pancreaticoduodenal fistula associated with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 25: 217.
- Van Minnen LP, Besselink MG, Bosscha K, Van Leeuwen MS, Schipper ME and Gooszen HG: Colonic involvement in acute pancreatitis. A retrospective study of 16 patients. Dig Surg 21(1): 33-38.
© 2019 Jiang Yan. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






